![]() For a Human Resources (HR) Department to play a strategic role within the organization, it needs to be proactive with its business processes/functions and how these impact the performance of the organization as a whole and how it adds an extensive value to the success, effectiveness, and efficiency of the organization. In this paper we shall present the HR business processes, whether such processes or functions are fully under the responsibility of HR or HR is partially involved in these processes. So, we can demonstrate the extent of the impact of HR on the Organization operational and financial performance. It is critical to understand that for HR to play its role within the organization, it needs to go beyond personnel record management, and start to view itself as a strategic partner within the organization. In order to achieve the goal, HR needs to understand its business process/functional scope and the extent to which it business processes impact the organization success or failure.
For a Human Resources (HR) Department to play a strategic role within the organization, it needs to be proactive with its business processes/functions and how these impact the performance of the organization as a whole and how it adds an extensive value to the success, effectiveness, and efficiency of the organization. In this paper we shall present the HR business processes, whether such processes or functions are fully under the responsibility of HR or HR is partially involved in these processes. So, we can demonstrate the extent of the impact of HR on the Organization operational and financial performance. It is critical to understand that for HR to play its role within the organization, it needs to go beyond personnel record management, and start to view itself as a strategic partner within the organization. In order to achieve the goal, HR needs to understand its business process/functional scope and the extent to which it business processes impact the organization success or failure.
HR Business Processes
In order to determine the scope of the functional and operational responsibilities of HR department within the organization, we have drawn up a list of business processes that are either under the direct responsibility of the HR department or where the HR department is involved. This list consists of twenty seven business processes/functions:
1. Organization Management
2. Job Classification
3. Clients Management
4. Projects Management
5. Competencies Management
6. Position Budgeting and Control
7. Recruitment
8. Hiring
9. On-Boarding
10. Probation Management
11. Employee Personnel Record
12. Leave Management
13. Resources Scheduling
14. Time Reporting
15. Payroll
16. Performance and Appraisals
17. Training & Development
18. Career Planning
19. Succession Planning
20. Benefit Planning
21. Health Care Planning
22. Risk Management
23. Health & Safety
24. Resignations & Termination
25. Off-Boarding
26. Compliance
27. Reporting
The above list of business processes can be used to demonstrate the strategic and operational importance of HR within the organization as some of these business processes have a direct impact on the business success in term of operational effectiveness and efficiency. In addition some of these business processes carry tremendous risk to the organization if not performed or inadequately performed. Such risks can cause great financial losses and/or legal implications for the organization.
If we survey HR departments in various organizations (employers/companies) to define the extent of their performance of the above business processes, we will find few HR departments do indeed perform all of the above business processes, while the majority may conduct few of the above business processes, namely those that are administrative in nature such as hiring, employee record keeping, and payroll. To name a few, the following are the primary reasons why the majority of HR departments are not performing all the business processes/functions in the above list:
- Clear set of administrative and operational policies that defines the business process and functional responsibility of the HR department
- Senior management lack of understanding of the role and responsibilities of the HR department and its impact on the performance of the organization as a whole
- Lack of trained resources (manpower) within the HR department to carry out most of the important and complex business processes within HR
- Lack of standards that provide a consistent framework and procedures to perform the said HR business processes
- Management misunderstanding of the effort in term of cost and return to the organization if the organization is to invest in the right resources to perform all the HR business processes
- The effort and cost required to effectively conduct all the above business processes/functions cannot be easily estimated as management requires an understanding of the cost versus the return on such an investment.
- Lack of systems and technology within the organization to empower HR with the tools to conduct these business processes
Having defined the HR business processes and the primary reasons why most of these business processes are not performed by the majority of organizations across the globe, the questions that arise are the following:
- Why should an organization conduct all these HR business processes/functions?
- What are the benefits and ROI to the organization from conducting all these HR business processes?
- What is the impact on the organization performance if only few of these business processes are conducted?
- How can HR department resolve the causes and address the reasons that are not allowing HR to conduct all these business processes?
In order to answer the above questions, we need to develop the following analysis tools:
- HR Business Processes Performance Impact Relationship Matrix – This matrix will show the relationship between processes and the operational performance impact of one process on the other.
- HR Business Processes Risk Analysis Matrix – The Risk Analysis matrix will be used to identify the Risk associated with each business process and its impact on the organization performance if the process is not, or partially conducted
- HR Business Processes Deployment Cost Matrix – This matrix will be used to rate the cost of deploying/implementing each process, so we can have an idea of the cost of the deployment of each process.
The above three matrices will be used to derive the HR Business Process Map that can be used by HR managers to demonstrate to the senior management of the organization the level of importance of each HR business process and the impact of the process on the organization goals, objectives, operation, clients, revenues, cost, and other business key performance indicators.
HRM Business Process Map
As previously stated, the HR Business Process Map is constructed from three matrices including the Business Process Performance Impact Relationship Matrix (BPPIRM) , the Business Process Risk Analysis Matrix (BPRAM), and HR Business Processes Deployment Cost Matrix (BPDCM). In this section, we shall build these three matrices and from which we will derive HR Business Process Map (HRBPM).
HR Business Processes Performance Impact Relationship Matrix
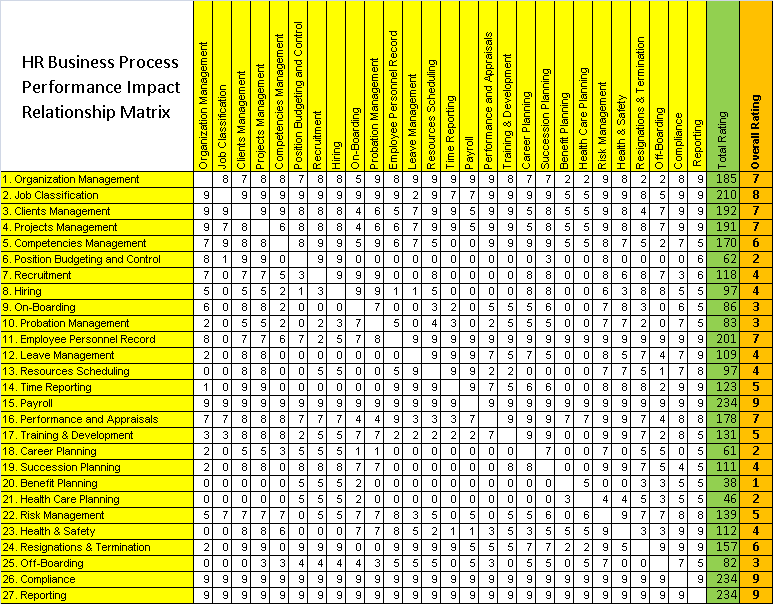
In order to build the PIRM, we need to have a metric that enables us to assess the degree of impact of one process on the other. The metric that we will be using is a measure/rating from 1 to 10, where the lowest assigned rating means the performance impact is low, and the highest means greater performance impact. Note that the rating you give to the impact of one process on the other is arbitrary and varies from organization to another depending on the organization industry, size, operation, and strategy. To reach the impact between two processes, P1 and P2, you need to ask the question, if P1 is not performed, or partially performed, can process P2 be performed. Table-1 below shows an example of a completed PRIM for an organization. Once the rating is completed between each two processes, then we sum all the rating to come out with total rating, then we divide the total rating by the number of processes, in this case 27 to derive the overall impact rating for each process. The higher the rating of the process, the most important is the process.
Table-1: HR Business Processes Performance Impact Relationship Matrix
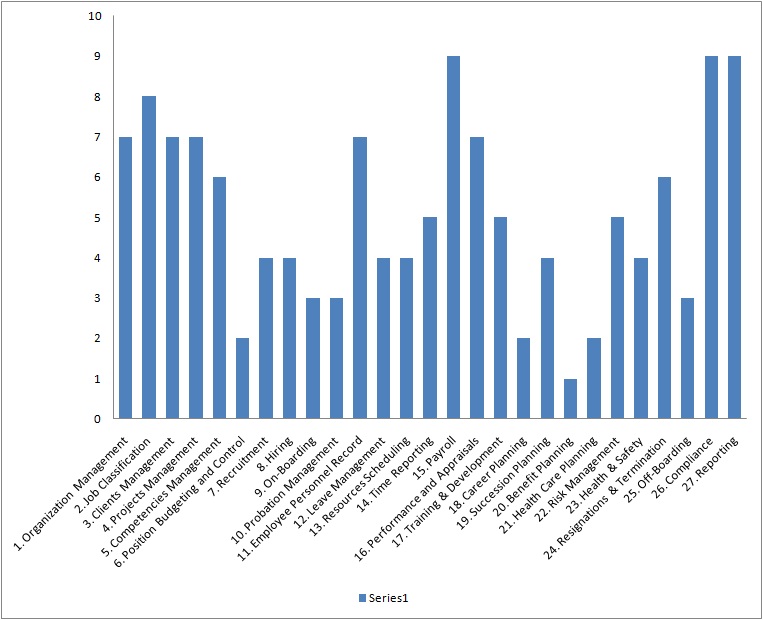
We have plotted the overall process relationship impact rating as shown in Figure-1. And what we can do further is to set a minimum impact threshold based on the overall rating. The minimum impact overall rating is used to decide which processes we can live without. For example if we set the minimum impact rating threshold as 3, then any process with overall rating below 3 is not critical. In the above example, based on 3 Rating Threshold, we can eliminate four processes:
- Position Budgeting and Control
- Career Planning
- Benefit Planning
- Health Care Planning
Figure-1: HR Business Processes Performance Impact Relationship Overall Rating
Again the impact overall rating threshold is arbitrary and depends on your organization. An example of the parameters that can be used to define the overall rating threshold are cost, risks, and ROI.
HR Business Processes Risk Analysis Matrix
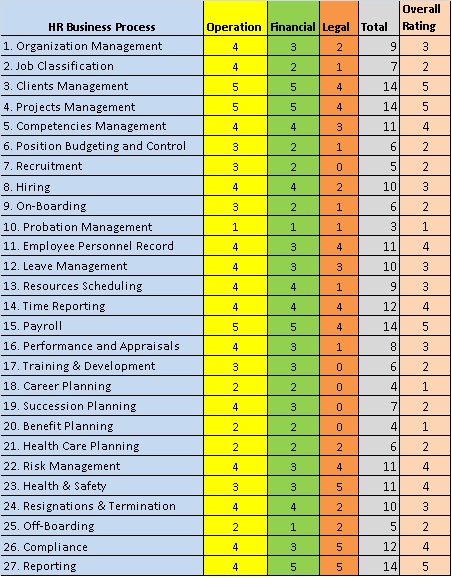
The HR Business Processes Risk Analysis Matrix is used to assess the operational, financial, and legal risks if an HR Business Process is not performed or partially conducted. The Risk metric that will be used to assess the risks includes the following categories/types of risks:
- Operational Risks
- Financial Risks
- Legal Risks
Note you can develop your own categories/types of risks, depending the requirements of your organization. Each of the processes will be rated on each of the above risk categories/types using a rating from 1 to 5. Note again that this arbitrary. You can define your own risk types and areas that are pertinent to your own organization and use your own rating range. Having defined the Risk types and rating to be used, we shall rate the Risk associated with the 27 HR processes. Again the highest the rate given to the process, the riskiest is the process.
HR Business Processes Risk Analysis Matrix
Table-2: Sample HR Business Processes Risk Analysis Rating
Again here we devise a minimum threshold based on the Risk Overall Rating as to what HR Business Process, the organization would like to perform and what process can be excluded from implementation. This is again arbitrary and depends on the organization risk mitigation strategy and plan.
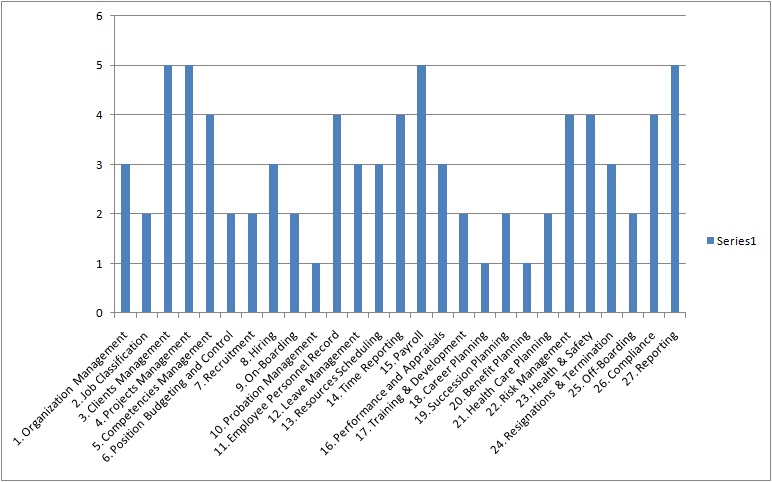
Figure-2: Sample HR Business Processes Risk Analysis Rating Graph
HR Business Processes Deployment Cost Matrix
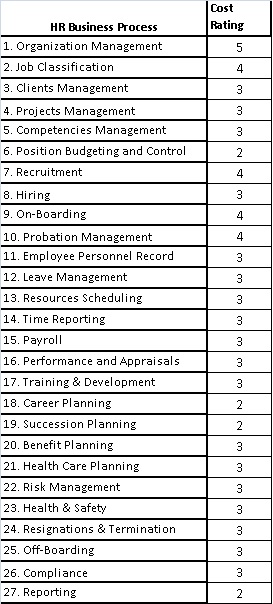
This matrix will be used to rate the cost of deploying/implementing each process, so we can have an idea of the cost of deployment of each process. Here again, we will use a metric based on an arbitrary rating that will be used to rate the cost of implementation of each business process. In our example we will use a rating range of 1 to 5. Where rating of 5 indicates the lowest cost and 1 indicates the highest cost.
Note the difference between the rating used for previous matrices and this matrix is that here we are giving a higher rate for those business processes with lower cost. The reason is that those processes with lower cost can be justified for implementation, while those processes with higher cost can be viewed for elimination, but this cannot be done using a threshold as in previous matrices. In this case rates need to be combined with the two previous overall rating to generate the final rating based on which a final analysis can be made.
Table-3 depicts the cost rating of each business process. Again the rating is arbitrary and depends the organization size, location, sate, country, and the cost of manpower and the complexity of the business operation.
HR Business Processes Deployment Cost Matrix
Table-3: Sample HR Business Processes Deployment Cost Rating
HR Business Process Map Rating and Analysis
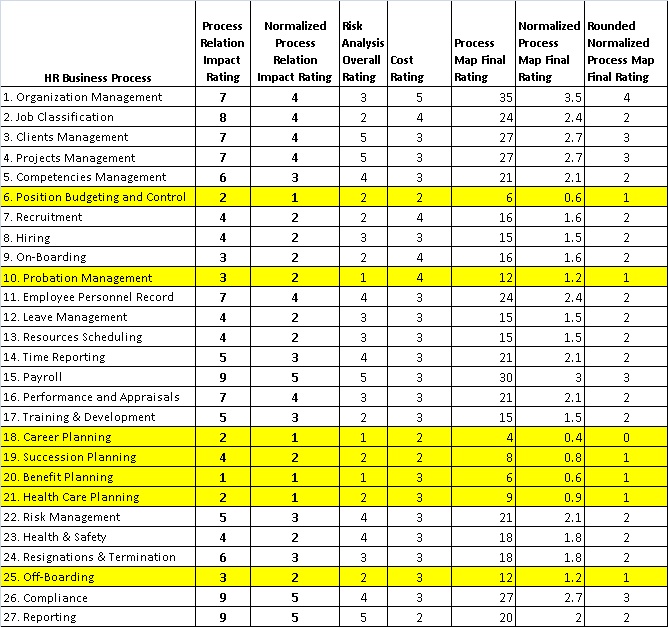
Now that we have constructed the three analysis matrices, we shall use them to construct the HR Business Process Map including the overall ratings derived from each matrix and calculate the final rating that can be used by the management to decide which HR Business Process is critical to the organization and which can be set aside for future implementation. Additional these final ratings can be used to provide an overall analysis to the senior management as to the scope of HR business processes and their impact on the business strategy, operation, performance, revenues, and cost.
Table-4 provides the HR Business Process Map and Final Ratings.
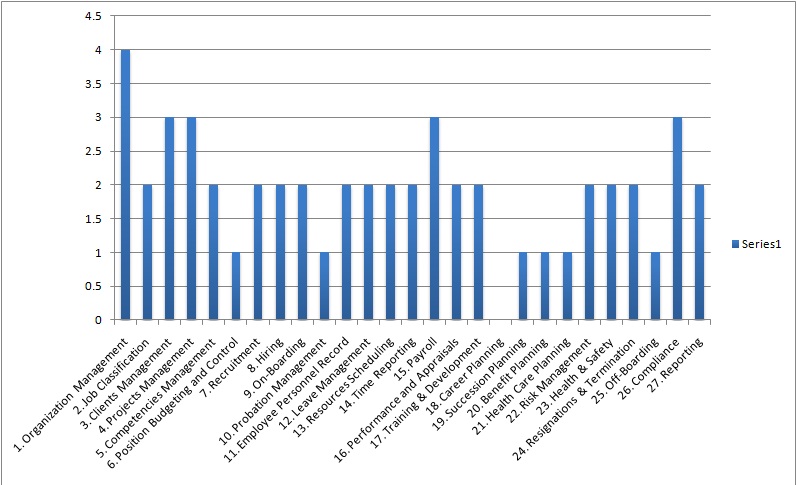
The above table and the graph below, show the final rating for each HR business process as derived from the three rating given in the business process impact analysis, risk analysis, and the cost analysis rating.
Figure-3: HR Business Process Map Rating Graph
Based on your organization requirements, you can set a minimum threshold to eliminate those HR business processes based on the final rating. In the example above, if we set the threshold as 2, then any business process with the rating below 2 will be eliminated. In this case, we will end up eliminating the following business process:
- Position Budgeting and Control
- Probation Management
- Career Planning
- Succession Planning
- Benefit Planning
- Health Care Planning
- Off-Boarding
Based, on the minimum threshold, we have eliminated 7 HR Business processes, and remained with 20 HR business processes that can be present to management for implementation.
Technology
Now that you have done your analysis by building the HR Business Process Map and the final rating of each HR business process, and eliminated those processes that do not have a significant impact on your organization, the next step is to assess various technologies to help you in the implementation of your HR Business Process Map. You need to find a Human Resources Management System (HRMS) that is integrated and that supports all of your HR Business Processes (HRM Process Map) out of the box. And this is not an easy task. There are a number of HR applications in the market that claim that they support all HR and Payroll business processes. But claim is not a true representation of what the product does and what it does not do. So, your first task is to present your HR Business Process Map with a detailed description of each process and have the HRMS provider demonstrate its product/solution against your HR Business Process Map to ensure that all your HR Business Processes are supported by the said HRMS. Additionally, you need to make sure that the HRMS product is a single integrated product, not made from multiple applications provided by a third party. The reason for this is that you want consistent user interface throughout all applications that support you HR Business Processes for each of use and ease of leaning (User Experience). The HRMS application and technology that you select must not only support your HR Business Process Map, but must be easy to use, easy to install, easy to implement and easy to support. And most of all you should have the choice to deploy the HRMS on premise, hosted, or in the cloud. Additionally, you need to assess the cost of licensing and implementation of the said HRMS and the return on your investment.