Overview
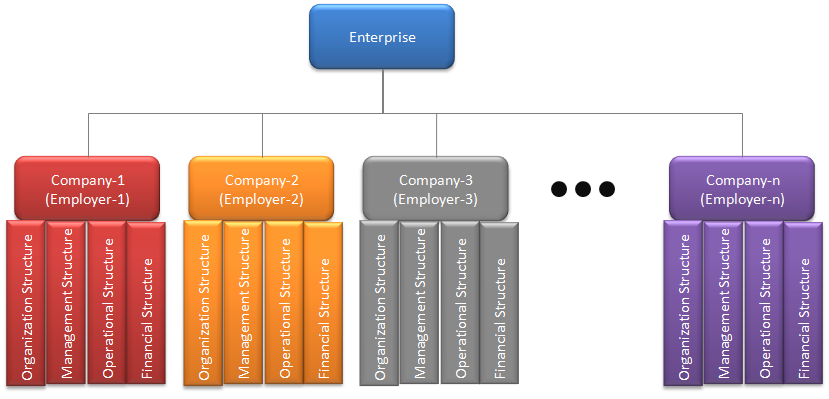
Interact HRMS including Core HR, Foundation Apps, Time and Leave Management, Payroll, and other applications can be Implemented and Deployed in support of single employer or multiple employers within a single enterprise. And Enterprise can be viewed as a group of companies, where each company is considered a single independent operating unit with its own organization, financial, operational and management structure.
Figure-1: Enterprise Structure
Each company within the enterprise is considered a separate employer as each company can have its own hiring, time and leave, and payroll policies. Example of an Enterprise, J&J Corp, which is a global diversified company, that owns four separate companies including J&J Retail, J&J Consulting Services, J&J Oil & Gas, and J&J Construction. Each of the four companies will have different structure and different HR and Payroll policies as their line of business is different. You can support such an enterprise in Interact using one Enterprise and under which you’ll have four companies/employers, each with its own separate Organization Structure, Job Classification, Chart of Account, and HR, Payroll, and related operational policies. Interact HRMS supports the implementation of multiple companies/employers using three models, which will be described in the remaining sections of this blog.
Implementation/Deployment Models
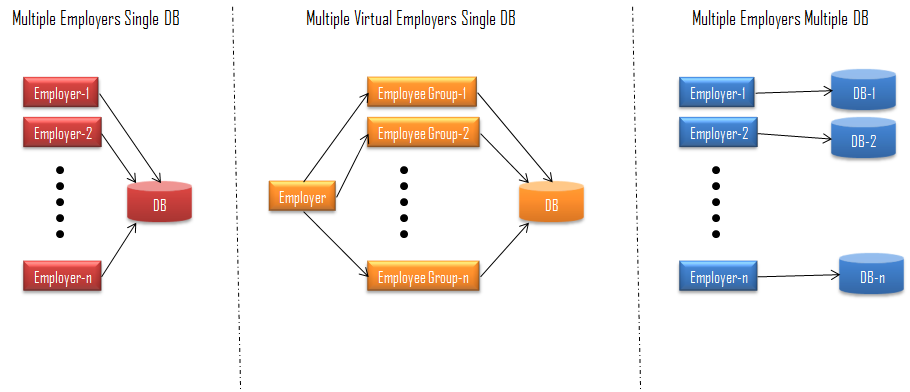
Interact HRMS supports three models to setup multiple companies/employers under the same enterprise:
Mode-1: Multiple Employers Single DB – In this model, multiple employers are created and they all share the same database. Each employer will have its own separate Foundation – Organization Structure, Job Classification, Employee Groups, Chart of Account Structure, GL Accounts, Banks, etc, Policies, and employee data. Though the employers/companies share the same database, one employer cannot view or access other employer’s data. Consolidation reporting and shared policies are defined at the enterprise level.
Model-2: Multiple Virtual Employers Single DB – In this model, multiple employers are created using Employee Groups and they share the same database. A single employer is created under the enterprise, and multiple Parent Employee Groups are created, each one will be used to represent an employer. Each Parent Employee Group representing an employer will have its own separate Foundation – Organization Structure, Job Classification, Employee Groups, Chart of Account Structure, GL Accounts, Banks, etc, Policies, and employee data. Though the parent employee groups share the same database, one employee group cannot view or access other employee groups’ data. Consolidation reporting and shared policies are defined at the employer level.
Model-3: Multiple Employers Multiples DB – In this model, multiple employers are created, each one with its own separate physical database. Each employer will have its own separate Foundation – Organization Structure, Job Classification, Employee Groups, Chart of Account Structure, GL Accounts, Banks, etc, Policies, and employee data. Employers/companies do not share the same database, and one employer cannot view or access other employer’s data. Consolidation reporting and shared policies are defined at the enterprise level. This model is used to implement SaaS, and it is the most optimal model for HR and Payroll Services Providers.
Figure-2: Implementation/Deployment Models
Models Encapsulation
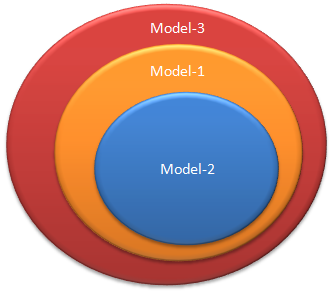
Implementing one model under another model, which is known as Models Encapsulation is supported, whereby:
- Model-2, Multiple Virtual Employers Single DB, can be implemented under Model-1, Multiple Employers Single DB
- Model-1, Multiple Employers Single DB can be implemented under Model-3, Multiple Employers Multiple DB
So Model-1 encapsulates Model-2, and Model-3, encapsulates Model-1, and Model-2.
Figure-3: Models Encapsulation
Single Software Instance
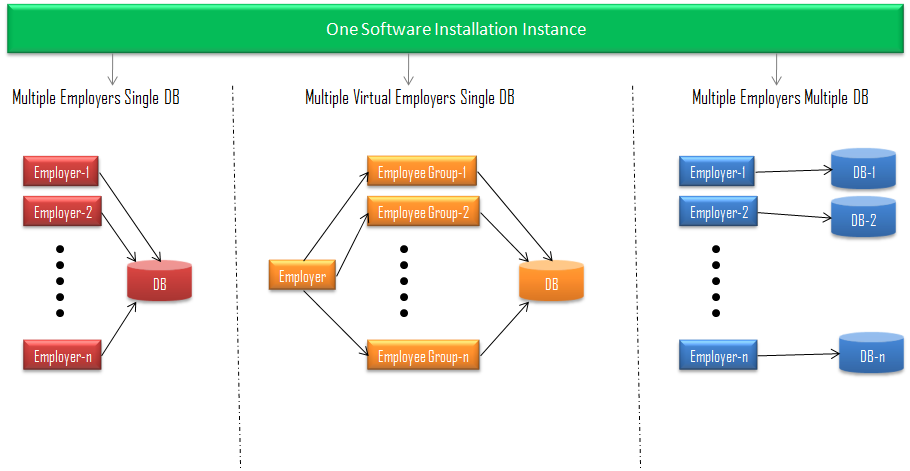
Implementing one or multiple models and creating and setting up multiple employers require single Interact HRMS software installation instance, which is shared by all models and employers created under the selected model. There is no need to install a separate instance for each employer. With the single installation instance approach, you’ll have less maintenance and administration overhead. And therefore less support cost.
Figure-4: Single Software Installation Instance
Models Setup and System Awareness of each Model
Implementation Models are setup either explicitly or implicitly. In the case of Model-3, Multiple Employers Multiple Databases, this is setup explicitly by activating the SaaS model setup at the Enterprise level, at which time, each time an employer/company is created, the system will create a separate database for the newly created employer. For the other models including Model-1 and Model-2, their setup is implicit. Under Model-1, when an employer is created and SaaS is not activated, the system, automatically share the existing database that is already used by other employers. Similarly under Model-2, when a Parent Employer Group is created and mapped to an Organization Unit that defines an Employer/Company, the system will automatically use the existing database that is being used by existing employers and parent employee groups.
Login Using Each Model
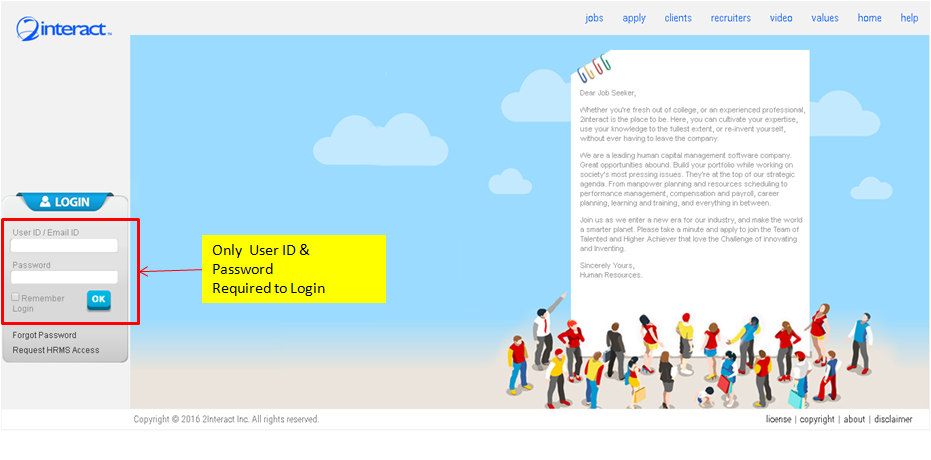
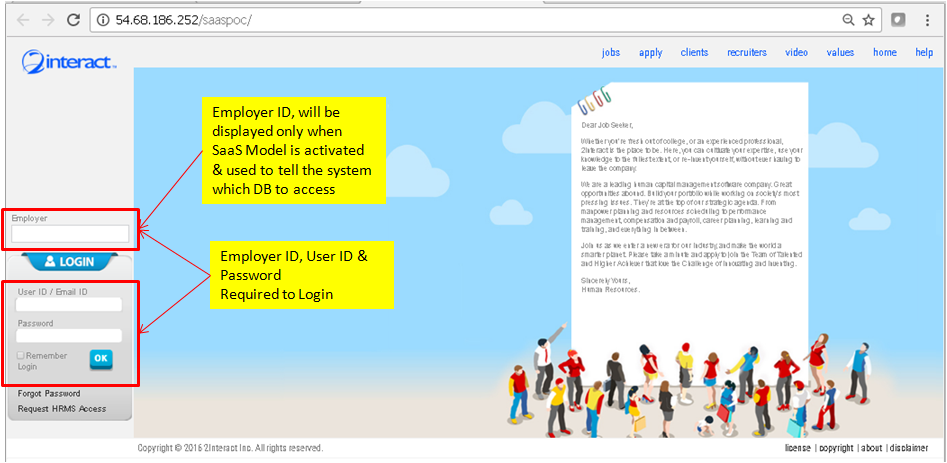
Under Model-1 and Model-2, the login to the employer is implicit, whereby the user needs to only supply a User-ID/Login-ID and Password, and system knows implicitly through the access control, which employer/company will be logged into. While under the Model-3 (SaaS), and since each company/employer has its separate database, the user needs to explicitly enter the Company/Employer iD, then User ID and Password. The Company/Employer ID is used to tell the system which database to access. Figure-5: Login under Model-1 and Model-2 (Implicit Login)
Figure-5: Login under Model-1 and Model-2 (Implicit Login)
Figure-6: Login under Model-3 (Explicit Login)
Conclusion
Interact HRMS provide three flexible Implementation and Deployment Models in support of multiple employers. Each model is optimal for specific setting and requirements. Model-1, multiple employers single database, and Model-2. Multiple virtual employers single database are optimal for HRMS and Payroll internal use by a company that has multiple entities/employers, while Model-3, multiple employers multiple databases is optimal for HR and Payroll Service providers. Additionally, these models are encapsulated, which provides additional setup flexibility and ease of management and administration. Further, there is no limit s to the number of companies/employers that can be created under each model. Finally, the single software installation instance in support of all three models and for unlimited multiple employers, makes the software easy to setup, maintain, and administer and use and lower the cost of support.